classes and objects
Suppose, there are two employees in our fictional company
- 🧑 -> Mark
- 👩 -> Maria
Mark properties:
- ID: 562
- Salary: 3000
- Department: Educational
Maria properties:
- ID: 561
- Salary: 5000
- Department: Software
employee class
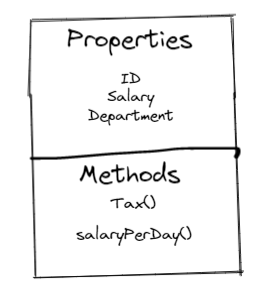
Properties
properties(or attributes) are variables that contain information about the object of a class. ID, Salary, department are properties of employee object
Methods
Methods are like functions that have access to properties of a class. They can accept parameters and return values.
class in Python
class myClass:
pass
obj = MyClass()
print(obj)
lets create our employee class
class Employee:
ID = 562
salary = 3000
department = "Educational"
Mark = Employee()
print("ID =", Mark.ID)
print("Salary", Mark.salary)
print("Department:", Mark.department)
another example:
class Employee:
# defining the properties and assigning them None
ID = None
salary = None
department = None
# cerating an object of the Employee class
Maria = Employee()
# assigning values to properties of Maria - an object of the Employee class
Maria.ID = 561
Maria.salary = 500
Maria.department = "Software"
Maria.title = "Tech Lead" # it is even possible add a new propertie outside the class
# Printing properties of Maria
print("ID =", Maria.ID)
print("Salary", Maria.salary)
print("Department:", Maria.department)
print("Tittle:", Maria.title)
Initializer
initializer is used to initialize objects of classes ps: it is a good pratice to define the initializers as the first member method in the class definition
example:
class Employee:
def __init__(self, ID, salary, department):
self.ID = ID
self.salary = salary
self.department = department
# creating an object of the Employee class with default parameters
Steve = Employee(356, 2500, "Human Resources")
print("ID :", Steve.ID)
print("Salary :", Steve.salary)
print("Department :", Steve.department )
Class and Instance Variable
In python, properties can be defined into two parts:
- Class variables
- Instance variables
class Player:
teamName = 'Liverpool' # class variables
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name # creating instance variables
p1 = Player('Mark')
p2 = Player('Steve')
print("Name:", p1.name)
print("Team Name:", p1.teamName)
print("Name:", p2.name)
print("Team Name:", p2.teamName)
references:
- Classes and Instances in Python -> https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hVtRA__K1Ik